How Abyss Improved Splash Zone Inspections with Lantern Eye™ Air (LEA)
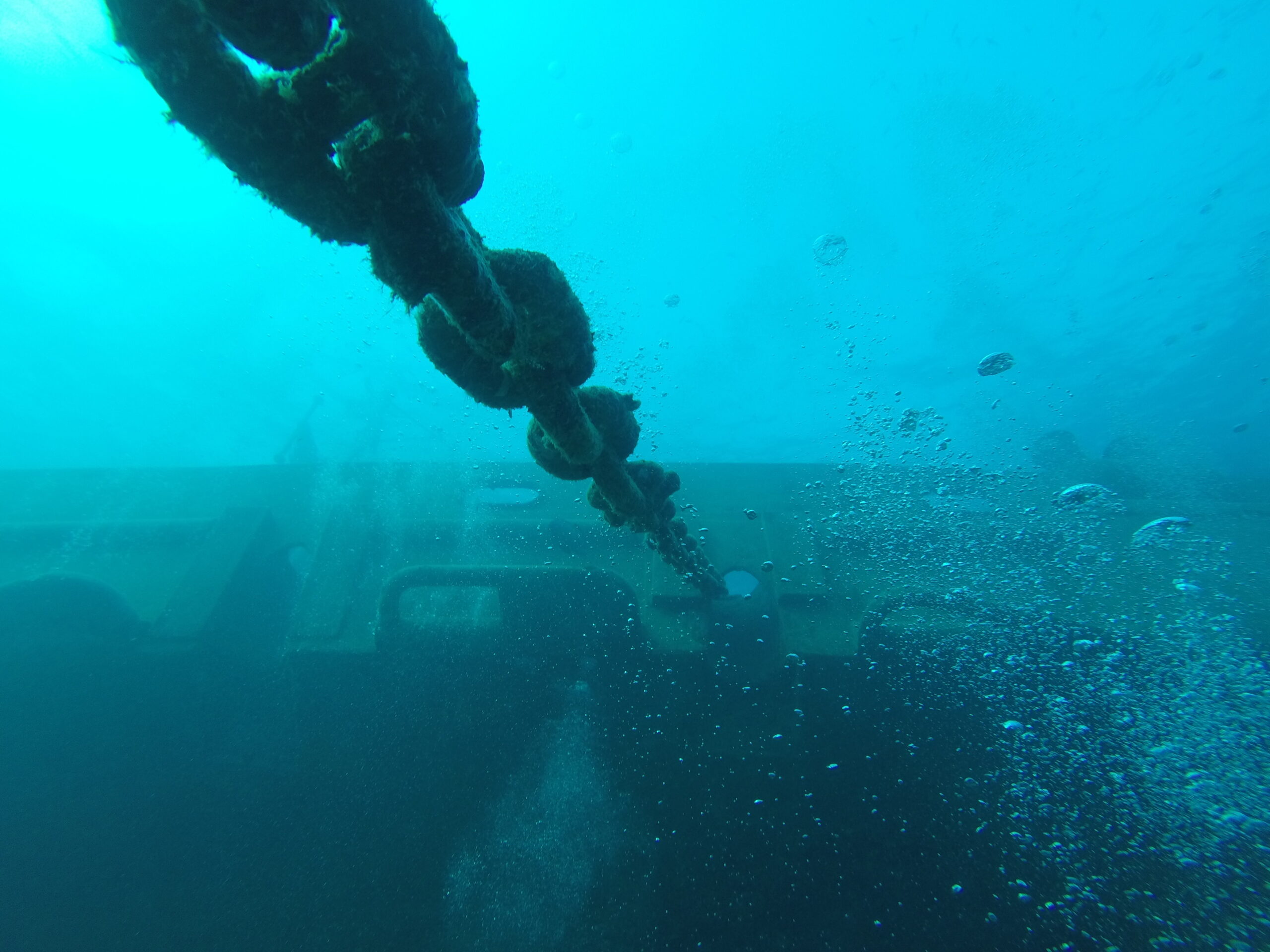
Abyss Solutions’ Lantern Eye™ Air (LEA) represents a significant leap in mooring chain inspection within splash zones. By utilizing optical stereo photogrammetric imaging, LEA transcends the limitations of traditional caliper-based methods, providing unprecedented accuracy and repeatability in measurements derived from 3D models.
Introduction
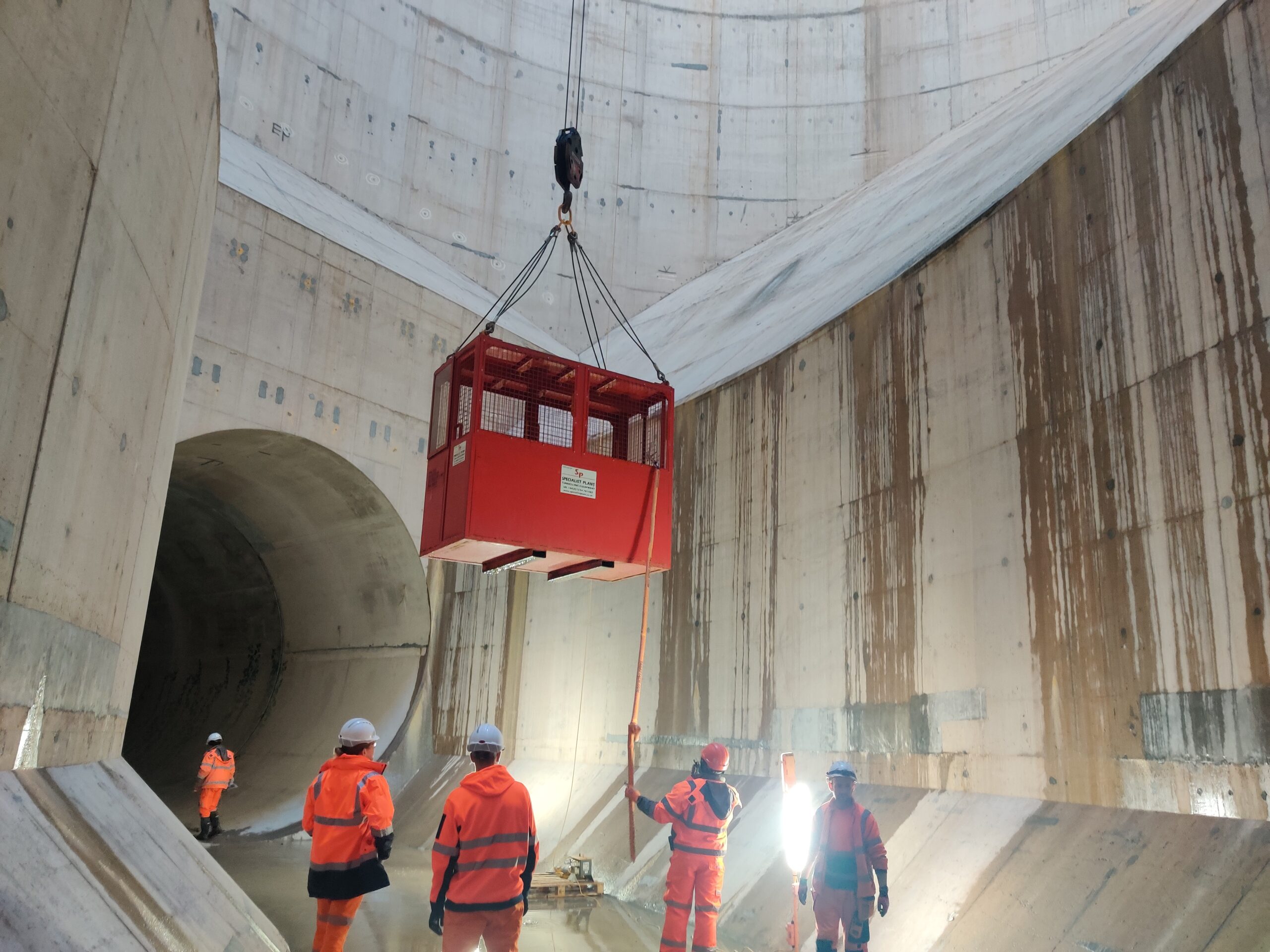
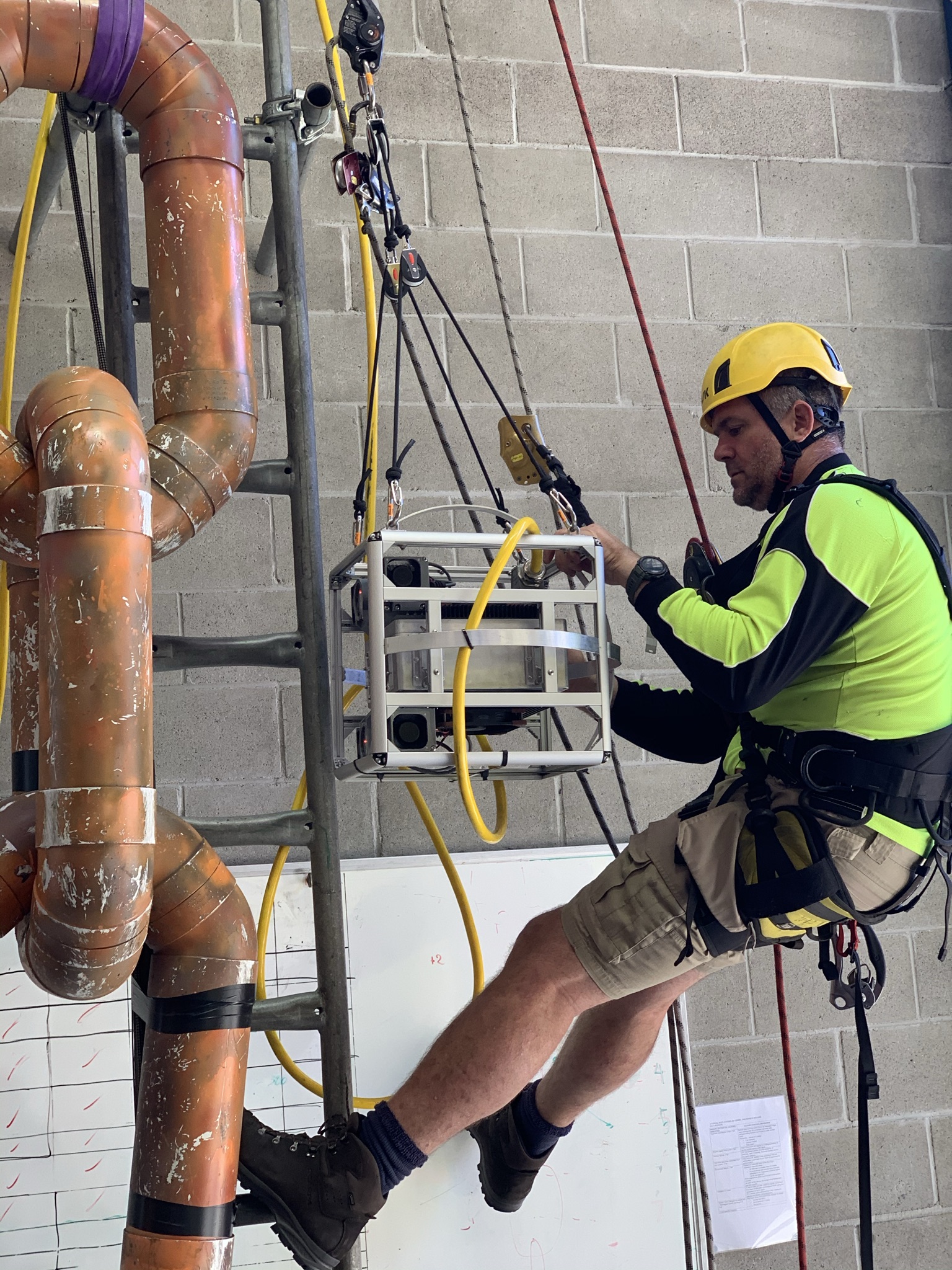
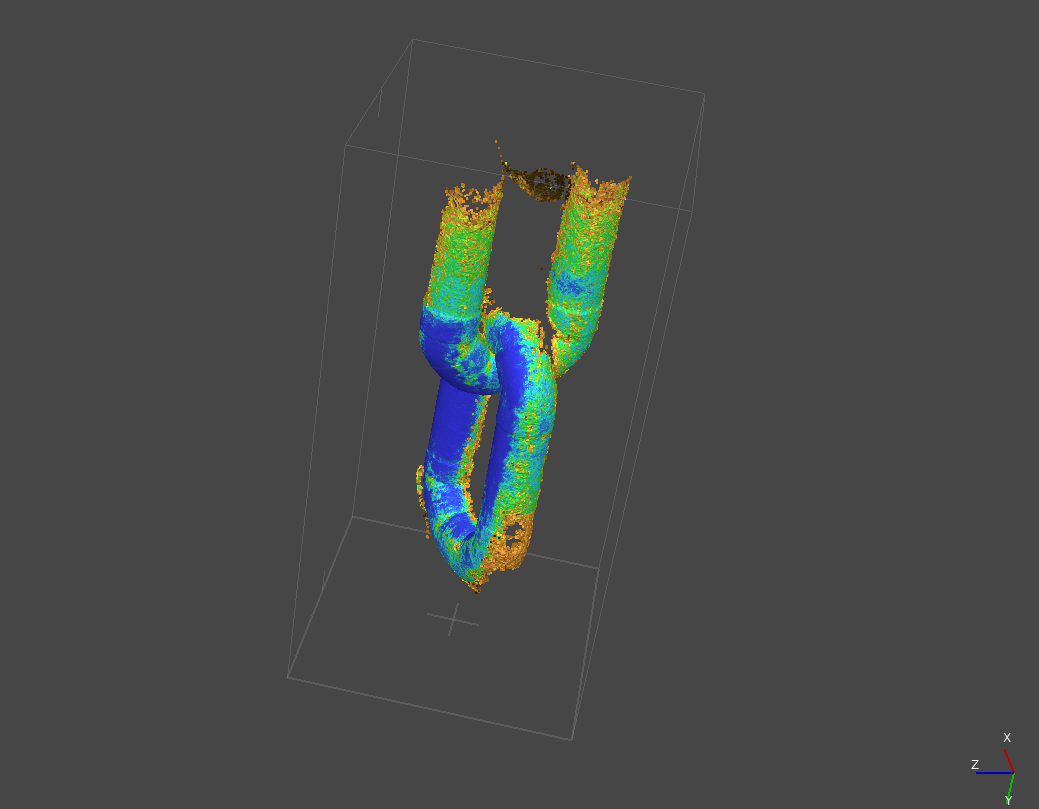
Abyss Solutions developed the LEA system, a novel approach to the inspection of mooring chains in splash zones. This system, deployable by a Rope Access Technician (RAT) team, captures high-fidelity images to create accurate, contactless measurements from 3D reconstructions.

Value to Customers
- Enhanced Accuracy: LEA offers a sub-1% error margin, significantly improving upon the inconsistency of manual caliper measurements.
- Operational Efficiency: The streamlined process reduces inspection time, leading to cost savings and minimized downtime.
- Data Reliability: Objective, repeatable measurements ensure consistent inspection results, vital for effective maintenance strategies.
- Safety Improvement: Contactless, remote operation reduces the risk associated with manual inspections in challenging environments.
Background
Traditionally, splash zone inspections are dependent on manual techniques, which are not only labor-intensive but also prone to human error. LEA’s innovative approach offers a solution that is both technologically advanced and user-friendly, overcoming these historical challenges.
Case-Study Scope
In this study, LEA was applied to inspect five chain links across four mooring lines, with its measurements rigorously compared against traditional caliper measurements to establish its precision and reliability.
Methodology
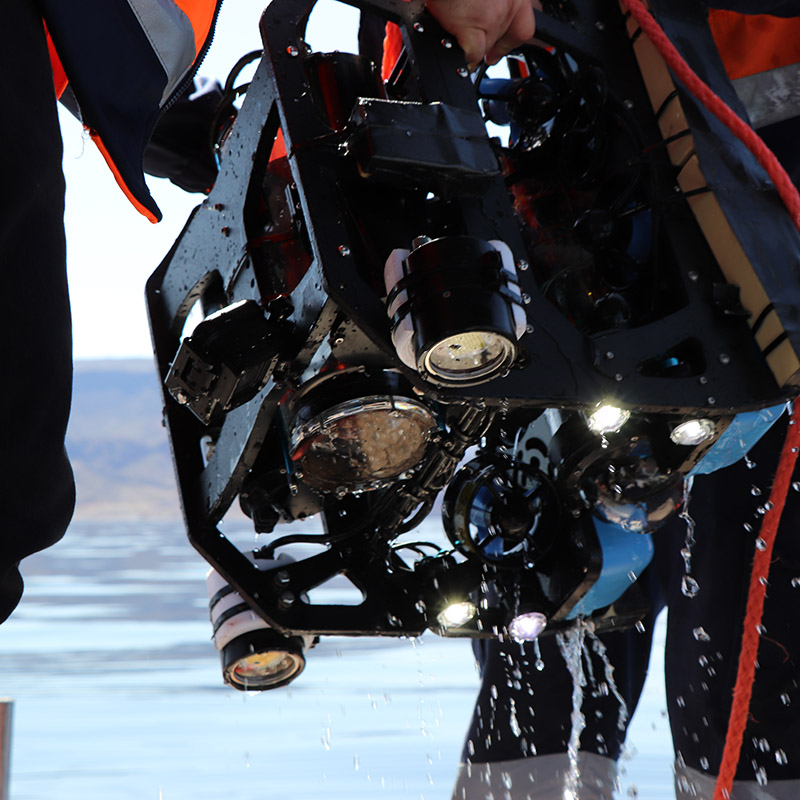
LEA’s advanced stereo camera system, complemented by high-powered strobe lights, was maneuvred around the chains by RAT personnel. This allowed for comprehensive imaging, which was then used to create detailed 3D models for accurate measurement analysis.
Results
LEA’s measurements of bar diameter and inter-grip length showed a maximum deviation of 1.7% and 0.9%, respectively, from caliper measurements. These results highlight LEA’s capability to match and surpass traditional methods in accuracy.